google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
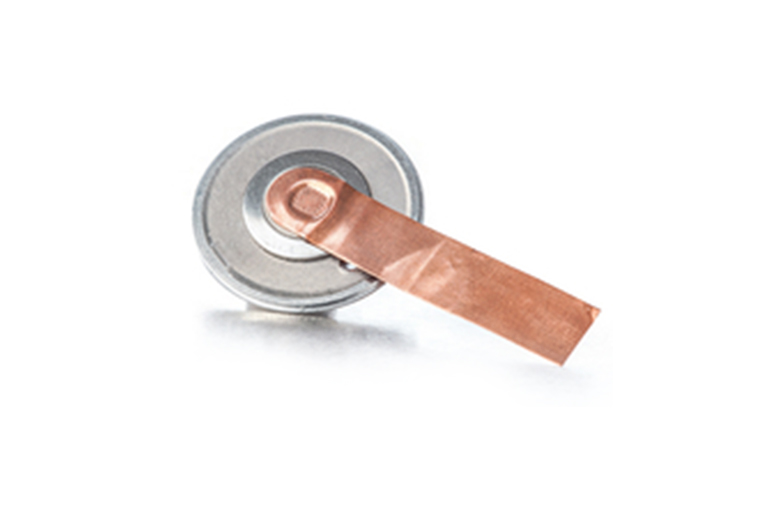
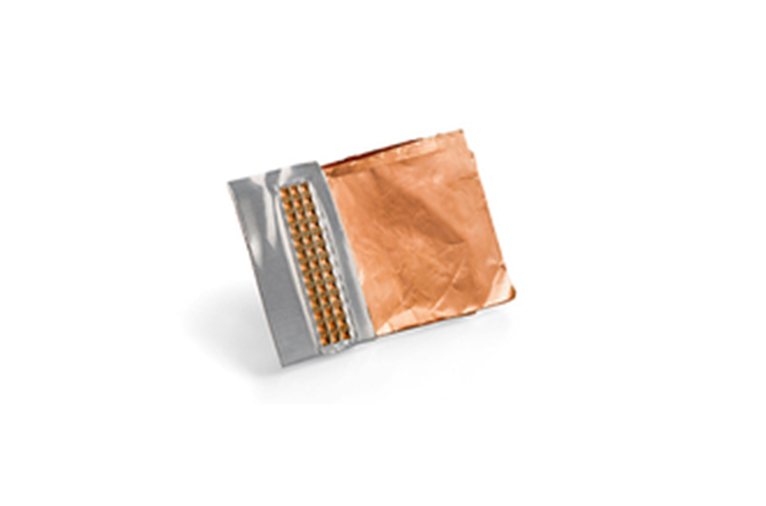
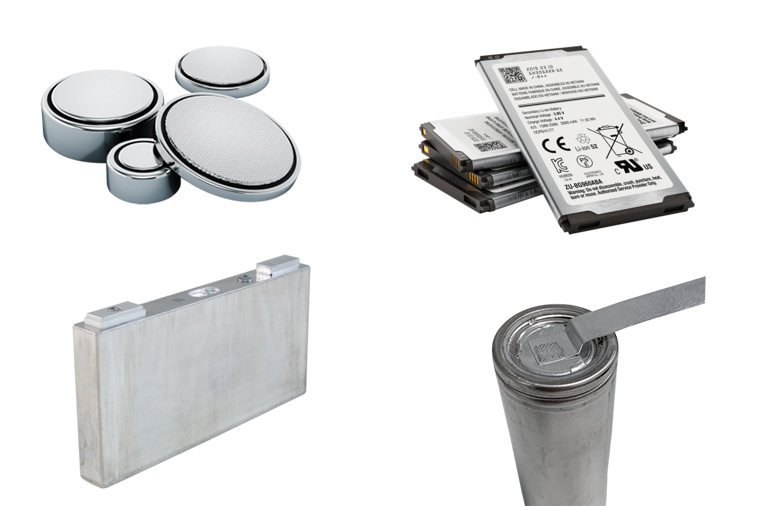



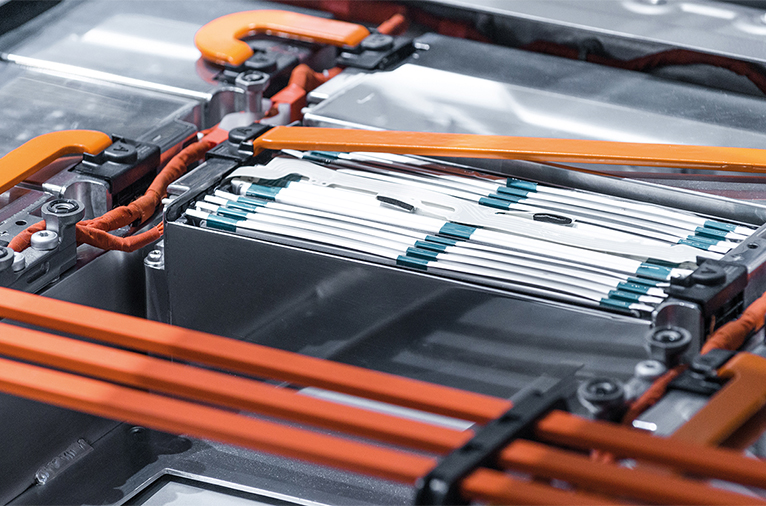

Lithium ion Battery (LIB)
Standard lithium-ion batteries (LIB) use copper foil for the anode and aluminum for the cathode. Typically, 20 to 60 foils are welded to each other, which requires a high level of bonding technology and long-term process reliability. Avoid burrs or cracks completely. As more and more products adopt rechargeable lithium-ion batteries (LIB), battery manufacturers are embracing ultrasonic welding as a reliable battery assembly method. This process specification requires the use of strong electrical contact and no particulate matter on the sealed film of the cell sheet.
Bagged battery and soft shell
Ultrasonic welding provides an alternative to thermal sealing of flexible LIB shells. The risk of battery damage can be minimized by shortening cycle times and using cold ultrasonic welding tools instead of thermal seals.
Battery management
The rapid development of new energy storage systems has put forward higher requirements for the reliable architecture of modern battery systems. State-of-the-art buses can transmit voltages up to 800 V and require minimal contact resistance to prevent over-hot spots.