google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
google-site-verification: google0228a1feb97d321e.html
Lithium battery technology is evolving from liquid to solid, with material innovation and manufacturing process optimization going hand in hand, while also focusing on green, low-carbon and global layout. In the next decade, all-solid-state batteries are expected to gradually become popular, while technologies such as sodium-ion batteries and lithium iron manganese phosphate will form a diversified market structure.

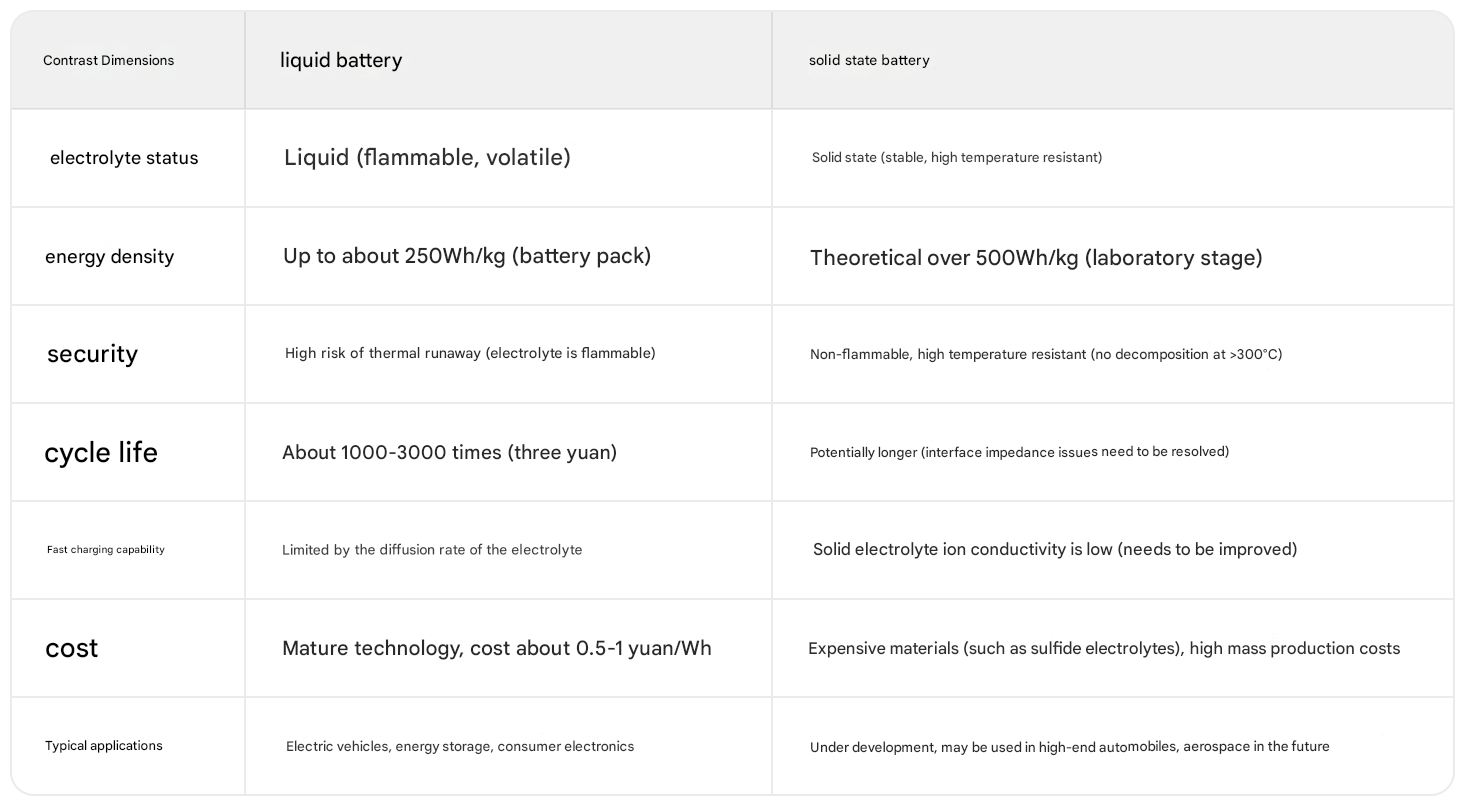
1. Liquid battery (traditional lithium-ion battery)
Lithium-ion batteries with liquid electrolyte as ion transport medium are widely used in electric vehicles, energy storage, consumer electronics and other fields.
Core structure:
● Positive electrode: such as ternary material (NCM) or lithium iron phosphate (LFP).
● Negative electrode: graphite or silicon-carbon composite material.
● Diaphragm: separates the positive and negative electrodes and allows lithium ions to pass through.
● Electrolyte: liquid organic solution (such as carbonates), containing lithium salt (LiPF₆).
● SEI membrane: solid electrolyte interface membrane formed on the surface of the negative electrode, protecting the electrode but increasing impedance.
2. Solid-state battery
Batteries that use solid electrolytes (such as ceramics, polymers or sulfides) instead of liquid electrolytes are the core direction of the next generation of battery technology.
Core structure:
● Positive electrode: high nickel material or lithium metal can be used.
● Negative electrode: metallic lithium (theoretical capacity is more than 10 times that of graphite).
● Solid electrolyte: It has both ion conduction and diaphragm functions, without the need for traditional diaphragms.
● No liquid electrolyte: Eliminates the risk of electrolyte leakage.
Application links and coating types of ultrasonic spraying
In lithium battery production, ultrasonic spraying technology is mainly used in the electrode preparation link of the front-end process:
1. Positive and negative electrode sheet coating
● Active material coating: The positive electrode slurry (such as lithium cobalt oxide, ternary materials) or negative electrode slurry (such as graphite) is evenly sprayed on the metal foil through ultrasonic atomization. Ultrasonic technology can accurately control the coating thickness (micrometer level), reduce material waste, and improve electrode consistency and energy density.
● Conductive agent and binder coating: Add conductive agents (such as carbon black) and binders (such as PVDF) to the active material, and enhance the conductivity and structural stability of the electrode through ultrasonic spraying.
2. Functional coatings
● Negative electrode protective coating: In view of the problem that traditional graphite negative electrodes are easy to expand, ultrasonic spraying can be used to coat elastic polymers or ceramic materials (such as Al₂O₃) to form a buffer layer, inhibit volume changes, and extend cycle life.
● Diaphragm modification coating: Nano-ceramic particles (such as boehmite) are coated on the surface of the diaphragm to improve the high temperature resistance and electrolyte wettability of the diaphragm and prevent short circuits.
In the future, solid-state batteries will take the lead in breakthroughs in new energy vehicles, energy storage, low-altitude economy and other fields, and gradually penetrate into consumer electronics and special equipment. It is expected to enter a full popularization stage after 2030, reshaping the energy storage pattern.